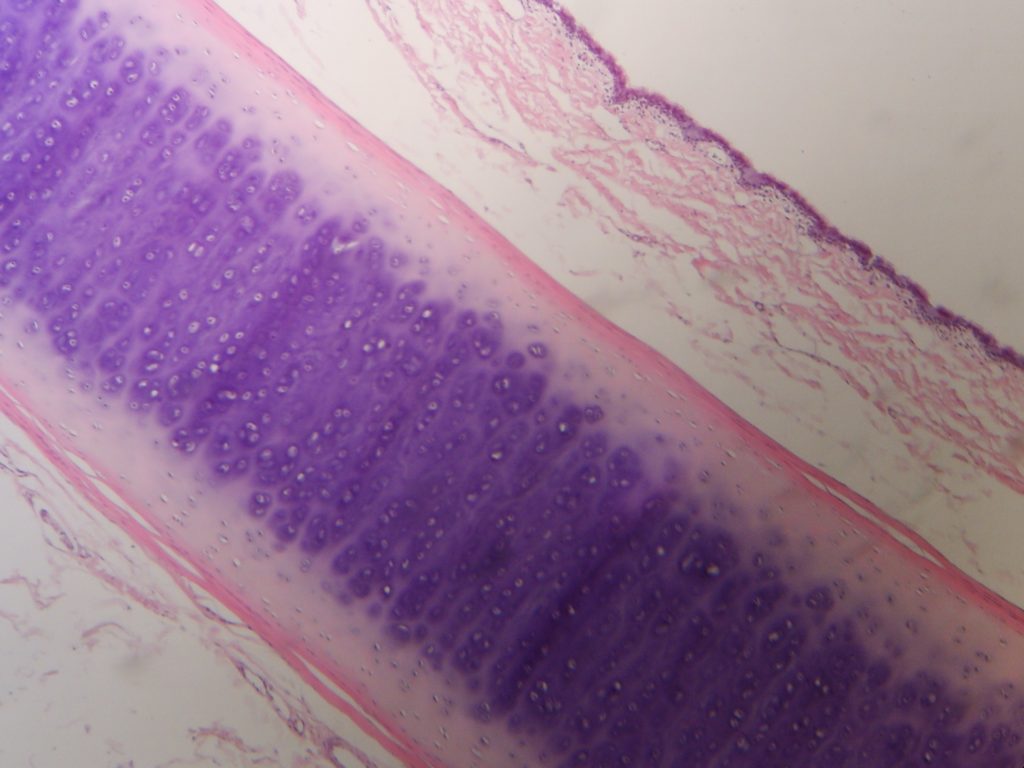
Perichondrium
The perichondrium is a dense layer of fibrous connecting tissue covering cartilage in different parts of the body.
These areas are often covered by Perichondrium tissue
- elastic cartilage in parts of the ear
- nose
- Hyaline cartilage in the larynx
- hyaline cartilage in the trachea
- epiglottis
- the area where the ribs connect to the sternum
- the area between the spinal vertebrae
Perichondrium tissue is not found in adult joints. It also doesn’t cover the areas where the ligaments attach to bone.
Perichondrium tissue can be found in articular cartilage in children. This is why cell regeneration is more common in children than adults.
The perichondrium has two layers.
- Extra fibrous layer. The dense connective tissue membrane contains fibroblast cells, which produce collagen.
- Inner chondrogenic layer. This layer is home to fibroblast cells, which produce chondroblasts (cartilage cells) and chondrocytes.
Perichondrium tissue protects bones from injury, especially those that are still developing or growing. It encourages cell renewal to speed up recovery. This is particularly true for children, but it may not hold for adults.
Perichondrium tissue provides elasticity to your body by reducing friction. This can help prevent injury and bone damage as well as long-term deterioration.
Perichondrium tissue’s fibrous structure allows blood to flow easily through your body. This constant blood flow distributes nutrients that nourish and strengthen your cartilage. Fibrous perichondrium tissue allows for oxygen and nutrients to flow freely without obstruction.
Conditions that impact the perichondrium
Your perichondrium tissue can be damaged by trauma to your cartilage. These are some of the most common injuries:
- Perichondritis. Infected perichondrium tissue can result. Insect bites? Piercings this injury can be caused by trauma, a common cause. This condition can be fatal if you are diagnosed. Pain, Redness, swelling, and/or reddening. You may also experience a complication called a Fièvre. You may also accumulate pus from your injury. Perichondritis may become a recurring condition. Antibiotics can be used to treat it.
- Cauliflower ear. This is a common injury that occurs in athletes and causes the eardrum to swell. A serious injury or a blow to the ear may cause damage to your perichondrium, reducing blood flow and causing permanent damage. The affected area of your ear will look like a cauliflower. Cauliflower ear may be treated with antibiotics or stitches if the doctor determines that there is an obstruction. This will increase blood flow.