Dyslipidemia Causes
Dyslipidemia Causes
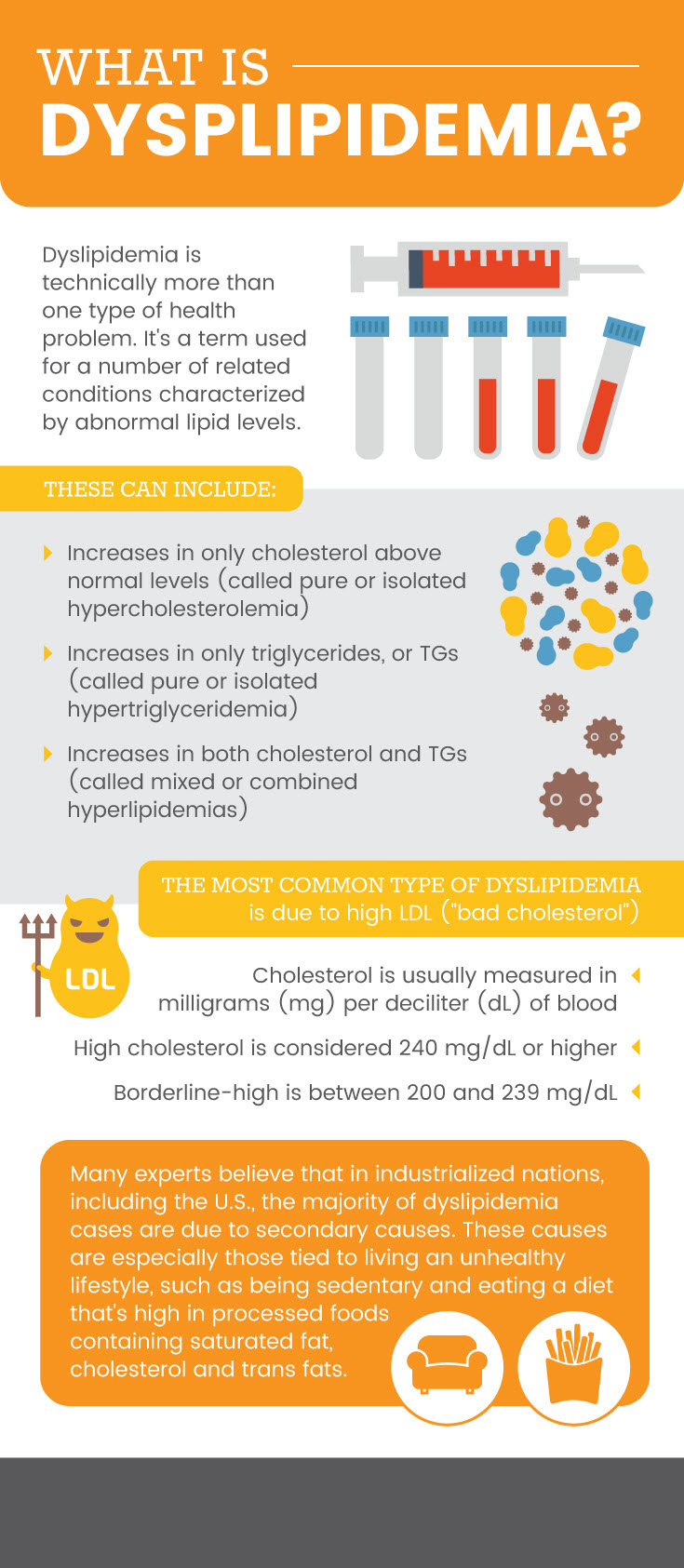
Dyslipidemia is a boost of plasma cholesterol, triglycerides (TGs), or both of them, or a deficient HDL cholesterol level that assists in the advancement of atherosclerosis.
Causation may be mainly (genetic) or collateral. The analysis is by calculating the plasma degree of combined cholesterol, TGs, and individual lipoproteins.
Procedure implicates dietary changes, exercise, and lipid-decreasing medicaments.
The aim for adults more than twenty years of age is to have cholesterol levels below 200 mg per deciliter (mg/dL).
Nevertheless, nearly ninety-nine million Americans are believed to have complete blood cholesterol levels bigger than this “healthy” range, based on the American Heart Association.
The Centers for Prevention and Disease Control (CDC) accounts that individuals with higher complete cholesterol have approximately twice the risk for heart disease as folks with perfect levels.
But less than half of adults with higher LDL cholesterol are receiving therapy to reduce their levels and reduce cardiovascular disease risk.
What exactly are the most typical causes of dyslipidemia (high cholesterol as well as high triglycerides)?
These include genetics and lifestyle habits – like eating a highly-processed diet, taking specific drugs, and being really sedentary.
Once dyslipidemia is identified, industry experts agree that making a lifestyle change to avoid additional problems needs priority number one.
Natural treatments for dyslipidemia can include:
- Taking measures to lower inflammation levels
- Improving the diet, frequently getting enough exercise
- Handling sources of physical and emotional stress
How about drugs used for treating dyslipidemia? Lipid-lowering drugs, while today recommended to huge numbers of adults, aren’t considered an excellent treatment option for lots of people.
Plus, they can result in a variety of side effects. But when an individual with dyslipidemia has a greater risk of developing cardiovascular disease, the doctor might believe that the effectiveness outweighs the poor when it involves the drugs’ consequences.
When needed – and after some other treatment methods have failed to assist – someone with dyslipidemia could need 1 or more drugs to avoid disease progression, particularly coronary heart disease.
What exactly are lipids?
Lipids are fat-soluble molecules, nonpolar organic solvents, and insoluble in water.
Lipids found inside the body are classified into 8 categories: oily acyls, saccharolipids, prenol lipids, sterol lipids, sphingolipids, glycerolphospholipids, glycerolipids, and polyketides.
- The root problem causing dyslipidemia is irregular lipid metabolism. Lipid metabolism is crucial for survival and has the natural processes known as soluble lipid absorption, lipogenesis, and then lipolysis.
- Lipid molecules have numerous roles within the entire body, so they’re important for life without being inherently bad. We absolutely need a specific amount of cholesterol for our health not to suffer.
- Lipids help with functions like as: offering power storage space, signal transduction, creating cellular structures, producing steroids and hormones, activating enzymes, supporting brain function, and taking in other nutritional lipids and also fat-soluble vitamins, which includes supplements A, D, K, and E.
- Cholesterol, as well as triglycerides, are toted all around the body within lipoproteins.
- The kinds of lipids connected with dyslipidemia include fats, triglycerides, phospholipids, cholesterol, and plant sterols. When amounts of these lipids fall outside the “normal range,” and then dyslipidemia is diagnosed.
Lipid absorption happens when fats are taken out of the diet.
Lipogenesis happens in the liver and adipose cells (body fat) and has fatty acid and triglyceride synthesis procedures.
Both of these’re controlled by diet changes and fluctuating amounts of sugar, glucagon, and insulin.
Lipolysis is the process of hydrolysis of triglycerides to fats and glycerol. The procedure is stimulated by beta-adrenergic molecules and curbed by insulin.
The job of dysfunctional lipid metabolic rate in causing dyslipidemia is a single reason eating a nutritious, anti-inflammatory diet that has a balance of fats is crucial for resolving the issue.
Signs & Symptoms of Dyslipidemia
Exactly how significant is dyslipidemia, and what kinds of problems may it cause?
There is a selection of hyperlipidemia disorders that people can develop, some worse than others.
When dyslipidemia is moderate, someone may have no symptoms at all (they are asymptomatic).
But others have a more serious case that may be life-threatening and require ongoing and immediate care.
When dyslipidemia symptoms do happen, the individual often also suffers from various other diseases/disorders regarding dyslipidemia.
These include vascular disease, coronary artery disease (CAD), stroke, and peripheral arterial disease. Symptoms are prone to include:
- Abdominal pain, vomiting, and nausea.
- Eruptive xanthomas (lesions of tiny reddish and yellow capsules), usually on the feet, the back, elbows, knees, or perhaps buttocks.
- Muscle and bone aches.
- Memory loss, misunderstandings, along with any other neurological problems in cases that are serious.
- A white, creamy look to retinal arteries & veins.
- Neuropathy.
- In some cases, symptoms related to heart problems or perhaps even strokes, like chest pains, numbness, difficulty breathing, and tingling in the arms.
Dyslipidemia is much more prone to result in problems when somebody has various other cardiovascular disease risk factors.
These risk factors can include a reputation for hypertension (high blood pressure), diabetes, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and a family tree of early coronary heart disorders (CHD).
Complications due to dyslipidemia can include:
- Higher risk for cardiovascular disease. Hyperlipidemia, the state which describes elevated plasma atherogenic lipoproteins and lipids, can lead to the development of plaque inside the arteries (atherosclerotic plaques), which increases the improvement of coronary artery disease and atherosclerosis (CAD).
- Having lower plasma levels of anti-atherogenic HDL cholesterol (sometimes referred to as “good cholesterol”) is related to a greater risk for heart disease.
- When triglycerides are elevated, greater risk for pancreatitis as well as hepatosplenomegaly.
Dyslipidemia Causes & Risk Factors
The root causes of dyslipidemia are hereditary (considered primary) and lifestyle-related (considered secondary reasons).
Many experts think that in industrialized nations, like the U.S., the vast majority of dyslipidemia cases result from secondary causes.
These reasons are especially those linked with following an unhealthy lifestyle, like being inactive and consuming a saturated diet plan in processed foods containing fat that is saturated, cholesterol, and trans-fatty acids.
Contributing factors that can result in dyslipidemia can consist of a single or even more of the following:
- Genetic inheritance. Specific gene mutations can cause defective clearance or overproduction of triglycerides, significant LDL cholesterol, or underproduction/excessive HDL cholesterol clearance.
- Some other existing health conditions that hinder regular lipid levels are vascular diseases, such as diabetes or obesity.
- The poor diet, like one loaded with processed foods, trans fats, fast foods, and fat that is saturated or perhaps cholesterol from junk sources. Trans fats are polyunsaturated or perhaps monounsaturated fats to what hydrogen atoms are included. Despite correlation with a selection of health problems, they’re currently utilized in numerous highly processed foods to enhance flavor, shelf life, and texture.
- A sedentary lifestyle with not enough exercise and exercise.
- High alcohol drinking.
- Kidney or liver disease.
- Hypothyroidism.
-
Use of particular medications/drugs, including thiazides, beta-blockers, retinoids, really energetic antiretroviral elements, cyclosporine, tacrolimus, progestins, and estrogen glucocorticoids.
- Cigarette smoking or overuse of tobacco/nicotine.
- Using anabolic steroids.
- HIV infection.
- Nephrotic syndrome.
Diabetes is a “significant secondary cause” of dyslipidemia.
This’s because research shows that a top percentage of diabetics – particularly those with type two diabetes – have a mix of higher TG, substantial little, dense LDL fractions, along with minimal HDL cholesterol.
Those with “diabetic dyslipidemia” are at excessive risk of acquiring complications when their condition isn’t well controlled.
For instance, complications are much more likely to develop if risk factors persist, like increased caloric intake, insufficient physical exercise, and excessive amounts of exposure to stress or toxins.
Conventional Treatment for Dyslipidemia
The aim of therapy for dyslipidemia is protecting against the further advancement of diseases including atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), intense coronary syndromes, stroke, transient ischemic attack, or perhaps peripheral arterial disease.
The physician can help identify you with dyslipidemia or perhaps rule the problem out by measuring the blood levels of different lipids.
A “total lipid profile” is based on calculating lipid and lipoprotein levels in the bloodstream, usually after a 12 hour fast.
Plasma lipids and lipoprotein concentrations typically assessed to evaluate dyslipidemia include complete cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, and triglycerides.
Depending on in case your symptoms point to any other disorders, the medical doctor might also need to evaluate amounts of fasting glucose, liver enzymes, creatinine, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), along urinary protein.
What Qualifies as Cholesterol that is high?
Based on the Merck Manual website:
You will find no numeric definitions of dyslipidemia; the phrase is put on to lipid levels that care has proven helpful. Evidence of benefit is strongest for lowering elevated low density lipoprotein (LDL) amounts … research is much less powerful for a gain from lowering elevated triglycerides and raising low high density lipoprotein (HDL) quantities.
Cholesterol is typically measured in milligrams (mg) of cholesterol per deciliter (dL) of blood. High cholesterol is recognized as total cholesterol levels of 240 mg/dL or even higher.
Borderline-high is between 200 and 239 mg/dL. Treatment is generally recommended when one or even a lot more of these risk factors apply:
- LDL cholesterol above seventy to 80 mg/dL (1.81 to 2.07 mmol/L) for folks with CVD and have multiple main risk factors.
- Extremely elevated TG quantities (> 500 to 1000 mg/dL or 5.65 to 11.3 mmol/L), particularly if combined with LDL cholesterol and decreased HDL cholesterol levels, or perhaps a solid family history of heart problems.
- LDL level above 100 mg/dL (2.59 mmol/L) in persons with diabetes.
Medications Used to Treat Dyslipidemia:
Treatments for dyslipidemia often include lifestyle changes – like making dietary changes and raising exercise – occasionally, along with taking several medications to deal with extremely high cholesterol or perhaps triglyceride levels, if needed.
The American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines endorse utilizing medication treatment for many groups of individuals at risk that is high for heart problems after a debate of contributing factors and the advantages of statin therapy.
- For higher LDL cholesterol, drugs that could be used include statins, bile acid sequestrants, ezetimibe, niacin, and potentially others. Statins are recommended for 4 groups of individuals, with virtually any of the following: identified ASCVD; LDL cholesterol ≥ 190 mg/dL; having an era between forty to seventy-five AND LDL cholesterol seventy to 189 mg/dL; and also estimated 10-year risk of ASCVD that’s more than 7.5 %.
- For high TGs, prescription drugs can include niacin, fibrates, omega 3 essential fatty acids, and occasionally others.
- While climbing HDL cholesterol levels may be ideal for several folks, that is not necessarily the truth. HDL levels don’t constantly predict cardiovascular risk and do not constantly have to be handled. For instance, when somebody has a genetic condition that leads to lower HDL levels, they’re not necessarily at any higher risk of acquiring cardiovascular problems in case they do not have other risk factors or perhaps poor lifestyle habits.
- If an individual has got the kind of dyslipidemia called chylomicronemic that’s causing acute pancreatitis, next they might have to be hospitalized or perhaps viewed within salinization.
5 Natural Management Tips for Dyslipidemia
1. Eat an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Nutritional intervention is often the mainstay treatment for individuals with dyslipidemia.
Some doctors will recommend their patients work on slimming down healthfully in case they’re obese or overweight.
But regardless of what a person’s fat is, they must always focus on making dietary improvements in case they’ve dyslipidemia.
While opinions differ in respect to the amount fat/cholesterol someone with dyslipidemia must-have in the diet of theirs, most authorities like the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute’s (NHLBI), suggest the following nutritional changes:
- Limiting consumption of soluble saturated fatty acids to approximately seven % or even less of total energy. It is advised that individuals with dyslipidemia limit cholesterol consumption to below approximately 200 mg each day.
- Getting between 25 35 % of the day’s total calories from consolidated sources of excess fat.
- Limiting salt ingestion to 2,400 mg one day.
Nevertheless, one of several things you must concentrate on most is staying away from processed foods, which increase cholesterol because of how they result in inflammation.
Good healthy fats shouldn’t be feared. But rather, the emphasis needs to be on along with high-quality sources included in a healthy diet.
Other than controlling the ingestion of some kinds of fats, diet-related changes to help lower cholesterol and triglycerides include:
- Eliminating foods like enhanced vegetable oils, potato chips, other snacks, cookies, sugary treats, bacon, processed meats, many low-quality standard milk products, and refined food grains.
- Boosting fiber consumption, particularly soluble fiber, from high-fiber foods as leafy green veggies; legumes and beans; artichokes; flax and chia seeds; nuts as walnuts and almonds; sweet potatoes and squash; avocado, pears, apples, berries, along with other fruits.
- Replacing processed carbohydrates — all those made with refined sugar and grains – with complex carbs. Examples include ancient whole grains, legumes, beans, whole fruit, along starchy veggies.
- Staying away from drinks and foods with concentrated high sugar and alcohol, like soda/soft beverages, packed desserts, sweetened milk products, etc.
- Having wild-caught fish 2 to 4 times per week to boost the intake of omega-3 fatty acids. This includes fish like salmon that is wild, halibut, trout, sardines, herring, and tuna.
- Consuming several calories will help you maintain the perfect selection of weight-based upon the level of yours and build.
If you’ve reduced HDL cholesterol (the sort many believe is the “good cholesterol”), you might be ready to increase the level of yours by consuming foods that are loaded with good fats, like real dark cocoa, eggs, grass-fed beef, and even fish.
2. Get Enough Appropriate Exercise
To help you lower inflammation, regulate stress hormones, and perhaps reach a better fat, regular physical exercise is usually recommended.
Daily exercise can reduce high LDL cholesterol in certain individuals and help keep ideal body weight.
And some scientific studies have found triglyceride concentrations can decrease by approximately thirty % after a person uses a regular workout program.
People with dyslipidemia who’re mainly sedentary often have to begin gradually and increase their exercise load slowly as their body changes.
Aiming to begin with approximately 30 60 minutes of moderate exercise each day, like walking or biking, swimming, is a great jumping-off point.
Lifting weights, dancing, yoga, or perhaps pilates are many other choices. Dealing with a personal trainer may also be extremely handy if you are working with some limitations and are uncertain precisely how to start.
3. Treat Contributing Health Conditions (Including Diabetes)
Treatment for dyslipidemia should include modifying underlying health problems that increase the danger of serious diseases, like hypertension and diabetic issues.
Lifestyle modifications are regarded as the very first step towards recovering from these kinds of common health issues.
Changes can include exercising, eating a nutritious diet, using supplements, or perhaps medications in case of beneficial, and limiting contact with toxins.
4. Limit Alcohol, Tobacco & Drug Use
Giving up smoking, not drinking huge quantities of alcohol, and never using any recreational drugs are essential to avoid progression.
These habits can add to various other health problems, like diabetes, liver, kidney problems, and improved inflammation, which all make dyslipidemia worse.
5. Use Supplements, if Helpful
- Fish oil — Has anti-inflammatory effects that could help avoid problems such as hypertension or perhaps high cholesterol, which are associated with heart disease.
- CoQ10 – May help control blood pressure.
- Garlic – May help to normalize blood pressure ranges.
- Lipoid acid – An antioxidant that protects against LDL oxidation plus hypertension. It can also help recycle various other antioxidants within the entire body, like glutathione, E, and vitamin C.
- Fiber supplements, including psyllium husks (although you might get results that are very similar from consuming a higher fiber diet), really help lower cholesterol amounts and protect the heart. It can assist with digestion and stopping overeating.
Final Thoughts on Dyslipidemia
- Dyslipidemia is a set of conditions indicated by heightened lipid levels, including elevated triglycerides and cholesterol.
- Individuals with dyslipidemia are at higher risk for atherosclerosis, peripheral arterial disease, and coronary artery disease.
- Causes of dyslipidemia include consuming a processed/poor diet with too much dietary intake of fat that is saturated, cholesterol, and trans fats; an inactive lifestyle; hereditary (familial) abnormalities regarding lipid metabolism; current health problems, which includes diabetes, kidney disease or perhaps liver disease; high alcohol consumption and smoking; as well as the use of certain medicines.
- Natural treatments for dyslipidemia can include improving the diet of yours, regularly getting plenty of exercises, and controlling sources of emotional and physical stress, which promote increased inflammation.

 Dyslipidemia Causes
Dyslipidemia Causes