Celtic Salt Benefits
Sea Salt
Sea Salt has been used as a natural flavoring for thousands of years, and it’s so vital to our existence that a portion of our tongues is even designated to taste saltiness.
However, in recent years, salt has come under fire and has been characterized as an unhealthy substance that we should cut out of our diets in favor of heart health.
That being said, not all salt is created equal. There is a difference between unrefined, mineral-rich varieties like sea salt versus normal ones that have been heavily processed and stripped of all of their natural nutrients.
So is it right for you? Does sea salt have iodine? And which types are best when it comes to your health? Keep reading for everything you need to know about this common kitchen ingredient.
What Is Sea Salt?
All types of salt — including table salt — originate from a sea or a salty body of water, but not all spices currently on the market come from the oceans.
What does that mean? Salts, not sea salt, are often derived from underground salt deposits left behind by seawater at some point.
Sea salt is a type produced from the evaporation of the current seawater. The drying is accomplished by open-air solar evaporation or a quicker vacuum evaporation process.
Some pricier sea salts available today often come from the slower sun-fueled evaporation method.

When you eat a sea salt that has experienced very little processing, you have a spice that contains health-promoting trace minerals.
It also has natural flavors and colors that make it much tastier and more enjoyable for cooking and homemade beauty products.
Sea salt can be unrefined or refined, although coarse sea salt is generally recommended to maximize its potential health benefits.
On the other hand, refined sea salt is washed to strip it of its trace minerals and often contains harmful food additives that trigger leaky gut.
Top 6 Benefits
1. Rich in Trace Minerals
High-quality sea salts typically contain upwards of 60 trace minerals; for specific types, like Himalayan sea salt, that number is closer to 84.
Either way, sea salts are a great source of micronutrients.
It’s become harder and harder to obtain trace minerals from our foods due to the lack of nutrient-rich soil.
However, trace minerals are still abundant in our planet’s seas and oceans, from which we get a variety of sea salts. (1)
2. Prevents Dehydration and Balances Fluids
Here’s how sodium works within the body: water follows salt, which means water retention also occurs if you increase your sodium intake too much.
Simultaneously, the opposite is also exact: a loss in sodium results in a decline in water, potentially causing symptoms like dehydration and extreme thirst.
By consuming sea salt in moderation daily, you also maintain sufficient sodium levels, balancing your sodium-potassium ratios.
Sodium and potassium are two electrolytes that work together to ensure proper fluid balance in your body’s cells, blood plasma, and extracellular fluid. (2)
3. Loaded with Electrolytes
The minimal processing of unrefined sea sodium chloride enables it to retain much of its original mineral content.
Sea sodium chloride contains many major electrolytes, like sodium, magnesium, calcium, and potassium, essential to good health.
Electrolytes have so many vital functions — from regulating your heartbeat to allowing your muscles to contract so that you can move.
Sea sodium chloride in moderation can help avoid an electrolyte imbalance, which can cause all kinds of severe negative symptoms, including some that are potentially deadly. (3)
4. Promotes Brain, Muscle, and Nervous System Function
As a good sodium source, sea salt is essential for proper brain, muscle, and nervous system function.
Not only does sodium play a role in regulating your body’s fluid balance, but it’s also required to transmit electrical signals in the body.
Why is this so important? Without the proper transmission of electrical signals in the body, so many things can get thrown off.
Without this communication system working as it should, the brain, muscles, and nervous systems are especially inclined to suffer.
Both too much and too little sodium cause cellular malfunction.
So as much as you hear about making sure you don’t get too much sodium chloride
in your diet, it’s also necessary to ensure we get enough. (4)
5. Supports Digestive Health
Not getting enough salt in your diet can also negatively impact your digestive health.
A lack of salt in the diet can reduce hydrochloric acid (HCL) in your stomach.
If you have low stomach acid, it can seriously throw your digestive system out of whack, contributing to issues like heartburn, stomach pain, vomiting, and constipation.
(5) Consuming the right amount of sea sodium chloride can help your body produce proper amounts of HCL since sea salt provides chloride, one of the building blocks of stomach acid.
6. Promotes Nutrient Absorption
Having enough stomach acid also helps our bodies to absorb vitamins and minerals like calcium, zinc, iron, folate, and vitamin B12.
For this reason, consuming high-quality sea sodium chloride
regularly can help your body absorb more nutrients from your foods.
This is excellent news since it’s not only what you eat but how your body processes what you eat that gives your body the essential nutrients it needs daily.
Types of Sea Salt
Many different types of sea salt are available, each of which varies based on its origins and the health benefits it provides.
Here are a few of the most common types of sea sodium chloride on the market today:
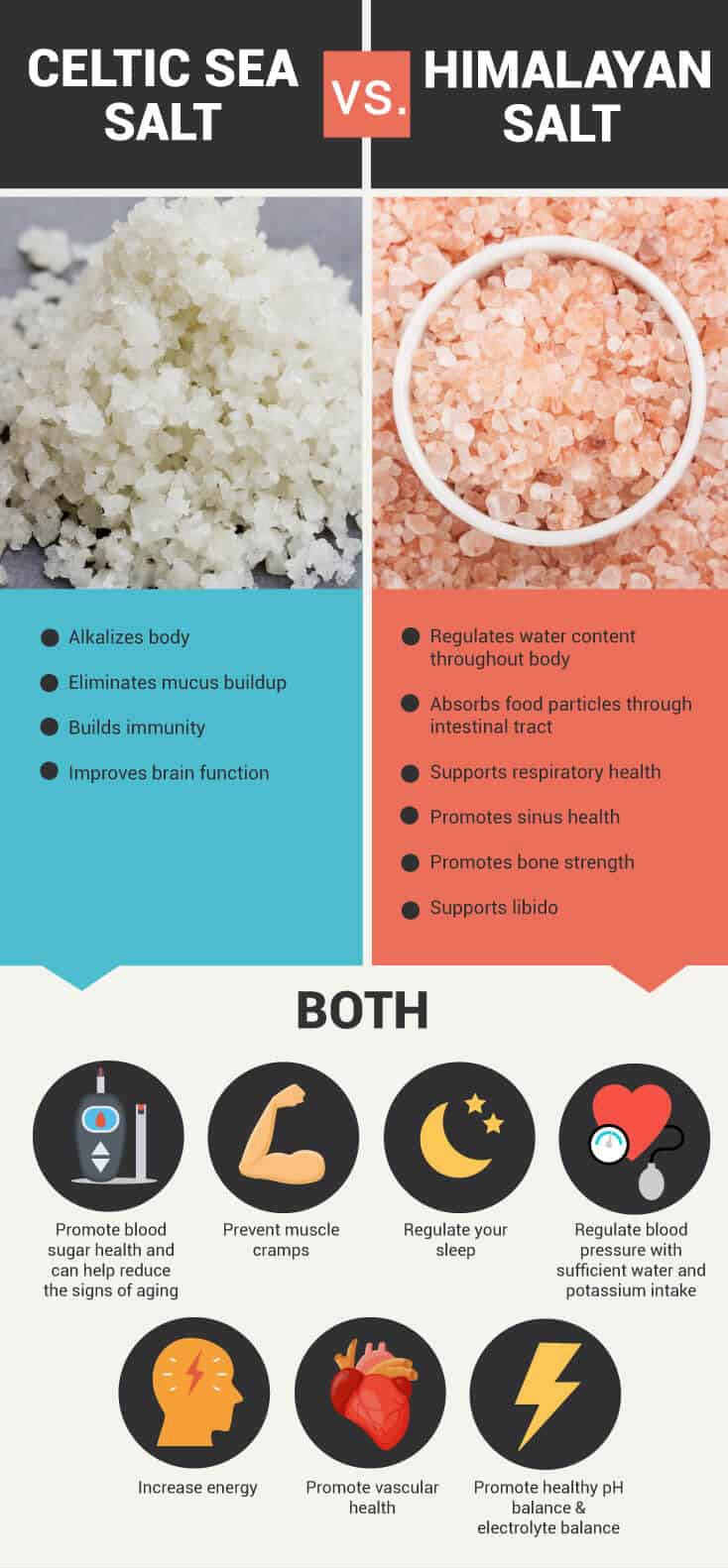
Himalayan Sea Salt
Many believe Himalayan sea sodium chloride is the purest salt available on the planet.
It’s believed to be composed of dried remnants of the original, primal sea with a history dating back to Earth’s creation.
Known as “pink gold” or “pink sea salt,” Himalayan crystal salt is a beautiful translucent pink with all the elements in your body.
Because of the fantastic nutrient load, doctors of functional medicine report that was regularly eating pink Himalayan sodium chloride can help:
- Regulate the water content throughout your body
- Promote healthy pH balance in your cells (particularly your brain cells)
- Promote blood sugar health and help reduce the signs of aging
- Assist in the generation of hydroelectric energy in cells in your body
- Absorb food particles through your intestinal tract
- Support respiratory health
- Promote sinus health
- Prevent muscle cramps
- Promote bone strength
- Regulate your sleep
- Support your libido
- Promote vascular health
- Regulate your blood pressure with sufficient water and potassium intake
Celtic Sea Salt®
Celtic sea salt, harvested using a 2,000-year-old Celtic method, is crucial to preserving its life-giving nutrition profile from the pristine waters off the coast of Brittany, France. It is a unique type of sea salt known for its distinctive grey color and rich mineral content.

Celtic sea salt is a natural source of trace minerals like magnesium, potassium, and calcium, essential for maintaining electrolyte balance, promoting healthy blood pressure, and supporting nerve and muscle function.
- Alkalize the body
- Balance blood sugars
- Eliminate mucus buildup
- Build immunity
- Improve brain function
- Increase energy
- Provide electrolyte balance
- Promote restful sleep
- Prevent muscle cramps
- Regulate heartbeat and blood pressure
Interestingly, this salt retains its moisture and is moist to touch, regardless of how you store it. Please think of this as a gentle reminder of its ocean source and continual life-giving properties.
Other sea sodium chloride options include:
- Fleur de Sel or Flor de Sal: French or Portuguese for “flower of salt,” this sea sodium chloride gets its name from the patterns of crystals that resemble flowers.
- This salt forms as a thin, fragile crust on seawater’s surface as it evaporates. Traditionally, it was used as a salve and laxative, but today it’s most commonly used for cooking as a finishing salt.
- Flake Sea Salt (or Flaky Sea sodium chloride): This variety of sea sodium chloride can be formed naturally or produced by various methods. Often sold under the brand Maldon sea sodium chloride flakes, flaky sea salts have thin, flattened crystals that provide more surface area with less mass resulting in a quick-dissolving and crunchy salt. It’s said that flake sea salt has a saltier taste but may contain fewer trace minerals than other sea salts.
- Hawaiian Sea Salt: Hawaiian or Alaea sea salt is a traditional Hawaiian salt. Alae is a natural red volcanic clay added to enrich the salt with iron oxide, and it also gives this sea salt its distinctive red sea salt color but can also be found in white or black sea salt varieties. Real Hawaiian salt is pricey and hard to find outside of Hawaii.
- Italian Sea Salt: This sea salt is derived from the Mediterranean Sea along the coast of Sicily.
You can also find other specialty sea salt varieties such as coarse sea salt, smoked sea salt, and iodized sea salt.
Scientific Evidence on Celtic Salt Benefits
While the concept of Celtic sea salt being inherently healthier than other salts is often promoted, concrete scientific evidence supporting specific health claims is limited. However, some preliminary research suggests potential benefits:
- Blood Pressure Regulation: A study published in the journal Nutrients in 2018 hinted at a possible link between Celtic sea salt consumption and improved blood pressure regulation in individuals with hypertension. However, more robust research is needed to establish a definitive causal relationship.
- Inflammation and Oxidative Stress: Research published in the journal Food & Function in 2017 explored Celtic sea salt’s potential anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. While the findings were promising, further studies are required to confirm these effects in humans.
It’s crucial to note that these studies are preliminary, and more comprehensive research is necessary to establish definitive health benefits of Celtic sea salt. Additionally, the overall sodium intake should be considered, as excessive sodium consumption can negatively impact health regardless of the salt type.

Sea Salt vs. Table Salt
Controversies surrounding Salt Intake and Heart Health
The relationship between salt intake and heart disease remains a subject of ongoing debate within the scientific community. While numerous studies have suggested a correlation between high sodium consumption and an increased risk of heart disease, hypertension, and stroke, other research has yielded less conclusive results.
Factors such as individual variations in salt sensitivity, overall dietary patterns, and the presence of other risk factors can complicate the interpretation of these findings. It’s essential to approach the topic with a nuanced perspective, recognizing that the optimal level of salt intake may vary from person to person.
Given the complexity of the issue, consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for obtaining personalized dietary advice. They can consider your specific health conditions, lifestyle factors, and medical history to provide tailored recommendations regarding salt intake.
Table salt and sea salt are two of the most common types of salt found on grocery store shelves and spice pantries alike. So, what are the differences between sea salt vs. table salt?
Table salt is mainly mined from underground salt deposits. It’s heavily processed to eliminate healthy minerals and is manufactured by taking natural salt (such as crude oil flake leftovers) and heating it to 1,200 degrees Fahrenheit. The chemical composition is wholly altered during this extreme process, destroying many potential health-promoting properties.
Although the salt chemical formula for both table salt and sea salt is mostly sodium chloride, the sea salt composition also contains more trace minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium. Generic table salt, on the other hand, ends up being about 97.5 percent sodium chloride and a 2.5 percent balance containing an array of ingredients, including:
- Anti-caking chemicals
- Iodine to prevent goiters
- MSG and white processed sugar to help stabilize the iodine
- Aluminum derivatives, such as sodium silicoaluminate
Most food manufacturers add iodine to table salt, increasing the risk of consuming excess amounts. While higher intakes of iodine are generally well-tolerated by most people, it could cause thyroid dysfunction for certain people who may be more sensitive to its effects. (6) For these individuals, keeping iodized salt intake in moderation is essential, and opting for a minimally processed, nonionized sea salt in place of iodized salt may be a good option.
Sea Salt vs. Kosher Salt vs. Rock Salt
Although kosher salt is another of the most popular types of salt available, few people understand its differences and the differences between kosher salt and sea salt.
Kosher salt stands out because of its large flake size and coarse texture, making it ideal for applying directly onto foods with your fingers.
Because of its unique taste, kosher salt is often used for draining blood from meat before consumption to comply with Jewish laws, which is where it gets its name.
On the other hand, rock salt is a type of salt derived from oceans that dried up millions of years ago, leaving behind a concentrated amount of salt in Earth’s crust. \
This type of salt contains a wide array of essential minerals and little to no moisture but is often classified as one of the purest forms of salt in existence.
Himalayan pink salt is one of the most famous rock salt examples, but other varieties are also available, which are harvested from different regions worldwide.
Sea Salt Uses in Ayurveda, TCM & Traditional Medicine
Sea salt has been a star ingredient in many forms of traditional medicine for centuries. Ancient Ayurvedic texts even mention sea salt and consider it essential to the body’s function and growth.
According to Ayurveda, salt should be unrefined and consumed in moderation to get the most health benefits. Sea salt is believed to act as an antidiuretic and help soothe the throat, clear the sinuses, support electrolyte balance, and aid in detoxification.
Meanwhile, in Traditional Chinese Medicine, sea salt is used to cool the body and regulate water and moisture levels. It’s also said to enhance kidney health, flush out toxins, and promote proper digestion in the body.
Where to Find & How to Use
Wondering where to buy sea salt? Given its rise in recent popularity, you can find a wide variety of sea salt brands at most major grocery stores in the spice and seasoning aisle. Pay close attention to the ingredients label and select a product with minimal added ingredients to make sure you’re getting the best quality possible.
Once you’ve got your hands on some high-quality sea salt, there are limitless ways to start adding it into your routine. One of the easiest ways is simply swapping it for table salt in your favorite recipes, using it to spice up main courses and side dishes. You can also add it to desserts for a savory kick of flavor by experimenting with recipes like sea salt ice cream or sea salt caramel.
Besides using it in cooking and baking, you can also try making some DIY beauty products with sea salt. Try making a dead sea salt scrub to get rid of dry skin by mixing coarse sea salt, coconut oil, and your choice of essential oils. You can also make a DIY sea salt spray for hair to get beachy waves all year round using just a few simple ingredients. For the best sea salt spray, combine sea salt with water and a bit of aloe vera gel in a spray bottle.
Sea salt is sometimes used for a sea salt flush or sea salt cleanse to help clear out the colon. This typically involves mixing lemon juice, sea salt, and water and downing it to produce a bowel movement.
History/Facts
Salt has always been essential to human life since humans need sodium to survive. The production of sea salt has been dated back to prehistoric times. Since all salt comes from dead, dried-up seas or living seas, the history of salt is equivalent to sea salt history.
In the sub-Sahara in the 6th century, Moorish merchants regularly traded prized salt in equal amounts (by weight) for gold.
Later in 1295, the explorer Marco Polo returned from his travels, telling stories of the imposing value of salt coins bearing the seal of the Great Khan of the Mongol empire.
There were salt trade routes worldwide, with the most popular one leading from Morocco south across the Sahara to Timbuktu.
The history of human civilization is said to be directly linked to salt. How so? Animals would create paths to salt licks; men would follow, turning trails into roads, and settlements would grow beside these roads.
As civilizations grew worldwide, salt continued to be one of the main items used for trade.
Solnitsata was Europe’s earliest known town, and it was constructed around a salt production facility. According to archaeologists, Solnitsata accumulated wealth by supplying salt throughout the Balkan Peninsula.
Sea Salt Precautions
Even though sea salt has some health benefits, you don’t want to overdo it. If your diet is too high in sodium, more water is excreted by the kidneys, which can cause complications with balancing other essential electrolytes.
It’s important to remember that even Celtic sea salt should still be consumed in moderation despite its potential health benefits. The American Heart Association recommends limiting daily sodium intake to no more than 2,300 milligrams (mg) for healthy adults and even less (1,500 mg) for individuals with high blood pressure, heart disease, or kidney disease.

Symptoms of having too much sodium in your diet may include bloating, lethargy, dehydration, weakness, irritability, and muscle twitching.
Hypernatremia occurs when there’s an imbalance of sodium and water in your body. This condition is more common among infants who have a low intake of breastmilk or consumption of formula that was not mixed properly, older adults, people with diabetes or kidney problems, severe burn patients, people who take diuretics, and those who eat heavily processed diets.
Symptoms can include intense thirst, headache, confusion, irritability, restlessness, and drowsiness. If you think that you may be experiencing hypernatremia, seek medical attention immediately.
Additionally, if you’re cutting table salt out of your diet altogether, it’s essential to ensure you’re getting iodine from other food sources in your diet. In addition to iodized salt, you can also find iodine naturally in foods like seaweed, dairy products, seafood, and eggs. If you don’t commonly consume any of these foods, opting for iodized sea salt may be an excellent option to make sure you’re meeting your daily needs for this crucial mineral.
Final Thoughts
- Sea salt is a type of salt produced from the evaporation of seawater. Because it’s less refined than other types of salt, it contains a higher concentration of trace minerals and a more intense flavor.
- Besides being less refined and containing a more vibrant nutrient profile, one of the main differences between table salt vs. sea salt is that table salt is often higher in additives and enriched with iodine.
- There are many different sea salt types, including Himalayan sea salt, Celtic Sea Salt®, Italian sea salt, Hawaiian sea salt, flake sea salt, and Fleur de Sel.
- The main difference between Himalayan salt vs. sea salt varieties like flake sea salt is that it is considered the purest form of sea salt and has a distinct pink color due to iron oxide.
- Several differences exist between sea salt vs. kosher salt, a type of salt favored for its large flake size and coarse texture.
- You can easily swap sea salt in for regular salt in your favorite recipes or try it in some beauty products by making a DIY sea salt hair spray or sea salt scrub to take advantage of its full range of benefits.











